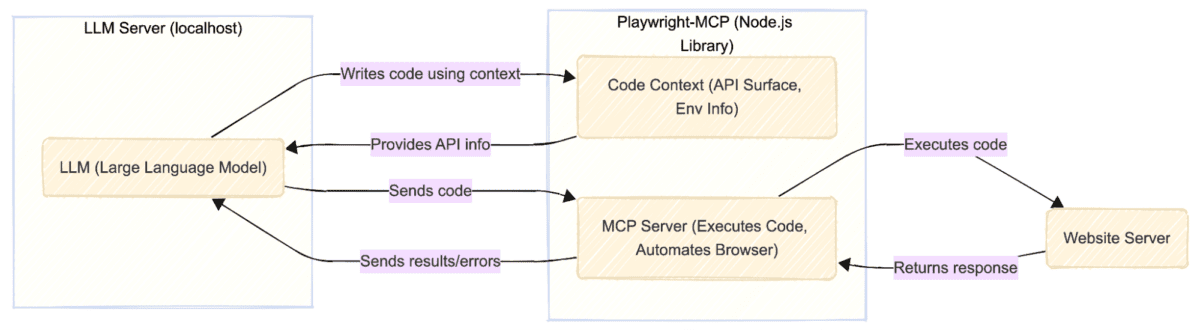
If you have ever built or used a webscraper, then you know how fragile its maintainability is. It requires overhead, checking website DOMs for updates, and sending alerts for any elements, classes, etc. that are no longer present. A small UI change on a website breaks your entire workflow. It’s the definition of a time sink.
Compare webscraping to a more intelligent system that can understand an objective and adapt how it interacts with the webpage based on the current DOM. One that adapts to the chaos of the internet. That’s what AI browser automation is all about. This isn’t just about making old tools smarter; it’s a fundamental shift in how we approach web automation.
We want to share the foundational ideas and actionable strategies for building your own adaptive web automation agents.
What is AI Browser Automation, and Why Does it Matter?
At its core, AI browser automation is the use of an autonomous software agent to get work done on the web. A traditional automation script is a series of hard-coded steps: a checklist of clicks, fills, and navigations. An AI agent, on the other hand, is given a high-level goal, like “find the market share data for our top five competitors,” and then it figures out the best way to achieve that goal.
For example: Playwright MCP will first use an accessibility snapshot of the webpage to formulate a plan, decide where to click, what to search for, and which information to extract. It might then use commands like browser_navigate, browser_click, and playwright_get_text_content to execute its plan without needing to know the elements of the page prior to execution.
It’s the difference between a self-driving car and one that’s stuck on a monorail.
With traditional automation, if the monorail track has a hiccup, the whole ride stops. With AI agents, the system can dynamically reroute and adapt to unexpected changes in website layouts or data structures, all while staying focused on the end goal. This is huge! It means less maintenance, fewer broken workflows, and a lot more time to focus on strategic work.
How to Implement AI Browser Automation
This new approach is all about moving past the limitations of older automation methods. Here’s a quick look at why AI agents are winning the race:
Adaptive by Design: Traditional scripts rely on fixed identifiers and rules. They’re blind to context. A new button on a page breaks everything. AI agents, however, are powered by computer vision and language understanding, allowing them to “see” a website like a human would. They can identify a “Submit” button, for example, even if its color, shape, or placement changes.
Built for Ambiguity: Older tools can’t handle anything that isn’t explicitly defined. You can’t tell a Selenium script to “figure it out.” AI agents, fueled by large language models, can reason and plan. They can handle a multi-step, complex task, deciding which path to take, what to do if an element isn’t found, and how to recover from an error, all without human intervention.
Complex Workflows: While old automation could do a single, long task, it struggled with workflows that required real judgment. AI agents can tackle open-ended, non-linear problems by decomposing them into smaller, manageable steps and executing them in a logical sequence.
Best Practices for AI Browser Automation
The good news is that getting started doesn’t have to be complicated. Here’s a playbook for a successful first deployment:
- Start Small and Specific: Don’t try to boil the ocean. Pick one repetitive task with a clear, measurable outcome. For instance, instead of a vague goal like "manage my social media," focus on a very specific, high-value task like "summarize customer reviews for our new product line every morning and post a sentiment analysis to Slack." This focused approach makes it easier to measure success and prove the value of the agent before you scale.
- Use the Right Tools: The AI ecosystem has a wide range of options for every skill level. If you're a non-technical user, low-code/no-code platforms like MindStudio and n8n provide visual builders and pre-built templates. For developers, open-source frameworks like LangChain and AutoGen give you the freedom to build custom systems from scratch.
- Build Evaluation from Day One: This is non-negotiable. Without a clear way to measure performance, you'll never know if your agent is actually helping or just adding to the complexity. For the "summarize customer reviews" example, a good metric would be the accuracy rate of the AI-generated summaries compared to human-written ones, or a simple reduction in the time a team member spends on the task.
- Mind Your Tokens: One of the most common (and expensive) mistakes with AI agents is not managing token usage. This can be a silent killer of your budget. Every time an agent interacts with a web page, it can be sending a huge amount of data to the model. To prevent this, you need to be smart about what information the agent consumes. Instead of giving it the entire web page, a good practice is to provide a "structured, lightweight representation" of the page's contents. This gives the model what it needs to make an informed decision without racking up a massive token bill.
Conclusion
The shift to intelligent, autonomous AI agents is not just a passing trend; it’s a fundamental change in how we get work done. For data teams, this represents both an opportunity and a responsibility. We are at a crossroads: we can either continue to be reactive, fixing brittle scripts as they break, or we can lead the charge toward a new era of automation.
The question isn’t whether AI agents will reshape how we work, but whether we will be the ones shaping that future or just reacting to it.

Need help building AI Agents for web automation?
If you’re looking to start building AI Agents but don’t have a solid plan or idea of where to start, attend one of our Free Generative AI Workshops for advice, direction, and help.
FAQs
How is AI browser automation different from traditional automation?
Traditional automation tools, like the scripted approach, rely on a strict, rule-based process. This is great for repetitive tasks that don’t change. AI browser automation, on the other hand, adds a layer of intelligence by using large language models to reason, adapt, and make its own decisions. While traditional automation is perfect for stable, predictable scenarios, AI agents excel in complex, dynamic environments. The two can often be used together to create a powerful solution.