In the era of massive data volumes and AI-driven projects, being able to transform data quickly and reliably has become essential for modern data teams. With a reliable, cloud-native integration platform for high-performance ELT/ETL, Matillion is at the forefront of this field. Even with the best solutions, data teams still face challenges such as maintaining consistency across environments, managing complex pipelines, and implementing stringent data governance regulations at scale. These manual, repetitive processes slow development and increase the risk of human error.
This is where Matillion’s Agentic AI, Maia, and Context Files come into play. While Maia automatically creates workflows that adhere to your organization’s standards, Context Files establish the single source of truth for those standards.
In this article, we will define Context Files and Maia, describe their relationship, and provide essential best practices for leveraging them together to achieve efficiency and governance in your Matillion DPC workflows.
Understanding Matillion Workflows
A Matillion workflow is a sequence of connected components, executed as an ELT/ETL job, designed to extract data from a source, load it into a cloud data platform (like Snowflake or Databricks), and perform transformations to prepare it for consumption. They are built visually using Matillion’s intuitive low-code/no-code designer.
If you’re new to Matillion DPC, check out this getting started guide.
What Are Context Files?
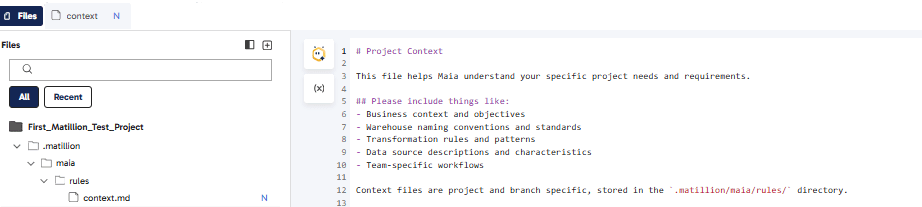
Context Files are the hidden layer of intelligence that informs your Matillion environment, crucially, Maia.
Context Files are structured metadata files, typically Markdown, that you embed within your Matillion project. They serve as a machine-readable organizational style guide and governance document. Context Files hold rules (e.g., All variables must be prefixed with dev
).
Matillion’s platform is designed to automatically scan and ingest the rules defined in these files. They reside in a dedicated project directory (.matillion/maia/rules/) and provide continuous, persistent context to every AI-driven action and every pipeline development effort.
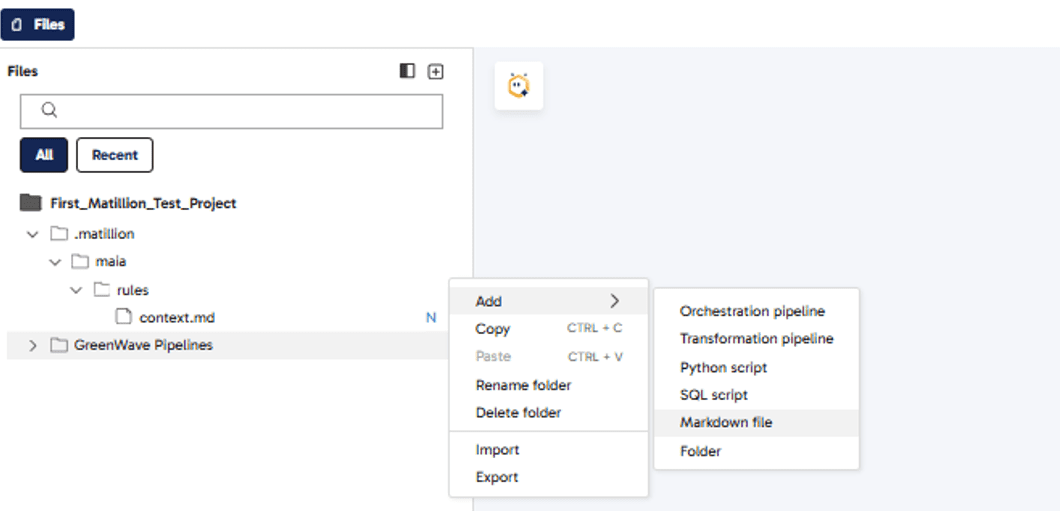
To create a new context file under Rules, click Add and select a Markdown file.
The screenshot below shows how the context file appears (This context file helps in generating documentation based on predefined rules).
If you’re new to Markdown, here are a few elements you’ll use in Context Files:
| Element | Syntax Example |
|---|---|
Heading 1 | # Title |
Heading 2 | ## Subtitle |
Bold | **bold** |
Italic | *italic* |
Unordered List | - Item 1 - Item 2 |
Ordered List | 1. First 2. Second |
Inline Code | `code` |
Table | | A | B | | --- | --- | | 1 | 2 | |
Introducing Maia
Maia is Matillion’s agentic AI, built directly into the Matillion Data Productivity Cloud. It’s a specialized team of AI agents—including the Data Engineer Agent (for generating, updating, and summarizing pipelines), Data Analyst Agent (for data sampling and data quality checks), Data Ops Agent (for Git-related tasks), and Operations Agent (for root cause analysis and troubleshooting)- designed to collaborate with human data teams to automate and accelerate all aspects of data pipeline work.
Maia’s primary function is to translate natural language prompts into operational, production-ready data pipelines, significantly boosting data team efficiency.
Pipeline Generation: You can ask Maia to
Build a pipeline to load historical data from your FTP, apply a data cleaning transformation (eg, NULL removal, etc.), and write it to the Fact table,
and it will automatically configure the necessary components, connections, and transformations.Governance and Consistency: Maia automatically reads and enforces the rules and standards defined in Context Files (such as naming conventions and design rules), ensuring that all generated workflows are compliant by design.
Analysis and Optimization: Maia can examine existing pipelines, explain their logic, diagnose potential configuration problems, and suggest performance improvements or bug fixes.
Step-by-Step: Improving Workflows with Context Files and Maia
Let’s see how we can develop a pipeline using a car sales business as our guide. In this scenario, your Context Files act as the brain of your project, containing all the information schemas, required KPIs with their exact formulas, and strict table naming conventions. By defining these rules once, you eliminate the need for repetitive manual instructions.
car-dealership-context.md
# Premier Group - Car Dealership Context
## Business Overview
Premier Group is a multi-location car dealership network operating across multiple showrooms.
We sell new and pre-owned vehicles from various manufacturers and track detailed sales metrics to optimize inventory, pricing, and showroom performance.
## Car Models & Submodels
### Luxury Sedans
**Mercedes C-Class**
- C200 Sport
- C300 AMG Line
- C43 AMG
**BMW 3 Series**
- 320i M Sport
- 330i xDrive
- M340i
**Audi A4**
- A4 Premium
- A4 S Line
- S4 Prestige
### SUVs
**Toyota RAV4**
- RAV4 LE
- RAV4 XLE Premium
- RAV4 TRD Off-Road
**Honda CR-V**
- CR-V LX
- CR-V EX-L
- CR-V Touring
**Tesla Model Y**
- Model Y Standard Range
- Model Y Long Range
- Model Y Performance
### Sports Cars
**Porsche 911**
- 911 Carrera
- 911 Carrera S
- 911 Turbo S
**Chevrolet Corvette**
- Corvette Stingray
- Corvette Z06
- Corvette ZR1
### Electric Vehicles
**Tesla Model 3**
- Model 3 Standard Range Plus
- Model 3 Long Range
- Model 3 Performance
**Nissan Leaf**
- Leaf S
- Leaf SV Plus
- Leaf SL
## Data Sources & Dataset Structure
### Primary Sales Dataset: `CAR_SALES_TRANSACTIONS`
**Location**: `SANDBOX.HNALAM.CAR_SALES_TRANSACTIONS`
**Schema**:
- `TRANSACTION_ID` (VARCHAR) - Unique transaction identifier
- `SALE_DATE` (TIMESTAMP) - Date and time of sale
- `CAR_MODEL` (VARCHAR) - Primary car model name
- `CAR_SUBMODEL` (VARCHAR) - Specific submodel/trim variant
- `SALE_PRICE` (DECIMAL) - Final sale price in USD
- `LIST_PRICE` (DECIMAL) - Original list price in USD
- `SHOWROOM_NAME` (VARCHAR) - Dealership location name
- `SHOWROOM_REGION` (VARCHAR) - Geographic region
- `SALESPERSON_ID` (VARCHAR) - Employee who completed sale
- `CUSTOMER_ID` (VARCHAR) - Customer identifier
- `VEHICLE_YEAR` (INTEGER) - Model year of vehicle
- `VEHICLE_CONDITION` (VARCHAR) - New or Pre-Owned
- `FINANCING_TYPE` (VARCHAR) - Cash, Lease, or Finance
- `DISCOUNT_AMOUNT` (DECIMAL) - Total discount applied
- `TRADE_IN_VALUE` (DECIMAL) - Trade-in credit if applicable
### Showroom Master Data: `SHOWROOMS`
**Location**: `SANDBOX.HNALAM.SHOWROOMS`
**Schema**:
- `SHOWROOM_ID` (VARCHAR) - Unique showroom identifier
- `SHOWROOM_NAME` (VARCHAR) - Dealership location name
- `SHOWROOM_REGION` (VARCHAR) - Northeast, Southeast, Midwest, West, Southwest
- `CITY` (VARCHAR) - City location
- `STATE` (VARCHAR) - State code
- `OPENING_DATE` (DATE) - When showroom opened
- `SQUARE_FOOTAGE` (INTEGER) - Showroom size
- `MANAGER_NAME` (VARCHAR) - Showroom manager
### Inventory Dataset: `CAR_INVENTORY`
**Location**: `SANDBOX.HNALAM.CAR_INVENTORY`
**Schema**:
- `INVENTORY_ID` (VARCHAR) - Unique inventory record
- `CAR_MODEL` (VARCHAR) - Primary car model name
- `CAR_SUBMODEL` (VARCHAR) - Specific submodel/trim
- `VEHICLE_YEAR` (INTEGER) - Model year
- `STOCK_DATE` (DATE) - When vehicle arrived
- `SHOWROOM_NAME` (VARCHAR) - Current location
- `STATUS` (VARCHAR) - Available, Sold, Reserved, Service
- `COST_BASIS` (DECIMAL) - Dealer acquisition cost
## Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
### Revenue Metrics
1. **Total Sales Revenue**
- Formula: `SUM(SALE_PRICE)`
- Aggregation: Daily, Weekly, Monthly, Quarterly, Yearly
- Dimensions: Showroom, Model, Region, Salesperson
2. **Average Sale Price**
- Formula: `AVG(SALE_PRICE)`
- Dimensions: By model, by submodel, by showroom, by region
3. **Gross Profit**
- Formula: `SUM(SALE_PRICE - COST_BASIS)` (requires join with inventory)
- Track: Per vehicle, per model, per showroom
4. **Discount Rate**
- Formula: `(DISCOUNT_AMOUNT / LIST_PRICE) * 100`
- Benchmark: Target < 8% overall
### Volume Metrics
5. **Units Sold**
- Formula: `COUNT(TRANSACTION_ID)`
- Aggregation: By day, week, month, quarter
- Dimensions: Model, showroom, region, salesperson
6. **Market Share by Model**
- Formula: `(Units of Model / Total Units) * 100`
- Track: Which models are most popular
7. **New vs Pre-Owned Mix**
- Formula: `COUNT by VEHICLE_CONDITION / Total COUNT`
- Target: 60% New, 40% Pre-Owned
### Efficiency Metrics
8. **Inventory Turnover**
- Formula: `Units Sold / Average Inventory Count`
- Target: > 6x per year
- Calculate by model and showroom
9. **Days to Sale**
- Formula: `AVG(SALE_DATE - STOCK_DATE)`
- Track per model and showroom
- Target: < 45 days
10. **Revenue per Showroom Square Foot**
- Formula: `Total Revenue / SQUARE_FOOTAGE`
- Benchmark showroom productivity
### Showroom Performance
11. **Showroom Sales Ranking**
- Rank by: Total revenue, units sold, profit margin
- Time periods: MTD, QTD, YTD
12. **Regional Performance**
- Aggregate: All metrics by SHOWROOM_REGION
- Compare: Year-over-year growth
13. **Salesperson Performance**
- Track: Units sold, revenue, average sale price per salesperson
- Rankings: Top 10 performers monthly
### Customer Metrics
14. **Financing Mix**
- Formula: `COUNT by FINANCING_TYPE / Total COUNT`
- Categories: Cash, Lease, Finance
15. **Trade-In Penetration**
- Formula: `COUNT(transactions with TRADE_IN_VALUE > 0) / Total COUNT`
- Target: > 35%
### Time-Based Analytics
16. **Sales Trend Analysis**
- Month-over-month growth: `((Current Month - Previous Month) / Previous Month) * 100`
- Year-over-year growth: `((Current Year - Previous Year) / Previous Year) * 100`
17. **Peak Sales Periods**
- Identify: Best day of week, best month, seasonal patterns
- Extract: Day of week, month, quarter from SALE_DATE
18. **Sale Price vs List Price Variance**
- Formula: `AVG((SALE_PRICE - LIST_PRICE) / LIST_PRICE) * 100`
- Target: < -5% (5% below list)
## Business Rules & Conventions
### Naming Conventions
- Tables: UPPERCASE with underscores (e.g., `CAR_SALES_TRANSACTIONS`)
- Staging tables: Prefix with `STG_` (e.g., `STG_CAR_SALES_TRANSACTIONS`)
- Fact tables: Prefix with `FACT_` (e.g., `FACT_DAILY_SALES`)
- Dimension tables: Prefix with `DIM_` (e.g., `DIM_SHOWROOMS`)
- Aggregate tables: Prefix with `AGG_` (e.g., `AGG_MONTHLY_SALES_BY_MODEL`)
### Date Dimensions
- Fiscal year: January 1 - December 31
- Reporting periods: Daily, Weekly (Mon-Sun), Monthly, Quarterly (Q1=Jan-Mar), Yearly
- Always include: SALE_DATE, YEAR, QUARTER, MONTH, WEEK, DAY_OF_WEEK
### Data Quality Rules
- SALE_PRICE must be greater than 0
- SALE_PRICE should be <= LIST_PRICE + 10000 (allow for add-ons)
- DISCOUNT_AMOUNT must be >= 0
- VEHICLE_YEAR must be between 2015 and current year + 1
- SHOWROOM_NAME must match master showroom list
- VEHICLE_CONDITION must be 'New' or 'Pre-Owned'
- FINANCING_TYPE must be 'Cash', 'Lease', or 'Finance'
### Performance Targets
- Overall discount rate: < 8%
- Days to sale: < 45 days
- Inventory turnover: > 6x annually
- Trade-in penetration: > 35%
- New/Pre-owned mix: 60/40
## Dashboard & Reporting Requirements
### Executive Dashboard (Daily)
- Total sales revenue (Today, MTD, YTD)
- Units sold (Today, MTD, YTD)
- Average sale price
- Top 5 models by revenue
- Top 5 showrooms by revenue
- YoY comparison
### Showroom Manager Dashboard (Weekly)
- Showroom-specific performance
- Salesperson rankings
- Inventory aging report
- Financing mix breakdown
- Discount analysis
### Monthly Business Review
- All KPIs aggregated by month
- Regional performance comparison
- Model mix analysis
- Trend analysis with previous 12 months
- Forecast vs actual
## Data Transformation Patterns
### Standard Aggregations
- Always include: YEAR, QUARTER, MONTH for time-series
- Group by: SHOWROOM_NAME, SHOWROOM_REGION, CAR_MODEL, CAR_SUBMODEL
- Common calculations: SUM, AVG, COUNT, MIN, MAX
### Date Calculations
- Extract year: `EXTRACT(YEAR FROM SALE_DATE)`
- Extract quarter: `EXTRACT(QUARTER FROM SALE_DATE)`
- Extract month: `EXTRACT(MONTH FROM SALE_DATE)`
- Day of week: `DAYNAME(SALE_DATE)` or `EXTRACT(DAYOFWEEK FROM SALE_DATE)`
### Common Joins
- Sales to Inventory: `ON TRANSACTION_ID = INVENTORY_ID`
- Sales to Showrooms: `ON SHOWROOM_NAME = SHOWROOM_NAME`
## Sample Data Values
### Showroom Names
- Premier Auto Downtown
- Premier Auto North Shore
- Premier Auto West Valley
- Premier Auto Airport
- Premier Auto Riverside
- Premier Auto Lakeside
### Regions
- Northeast
- Southeast
- Midwest
- West
- Southwest
### Typical Price Ranges
- Economy: $20,000 - $35,000
- Mid-range: $35,000 - $55,000
- Luxury: $55,000 - $95,000
- Sports/High-end: $95,000 - $200,000+
---
**Note**: This context file should be referenced when building any pipelines,
dashboards, or analytics related to car sales data. All KPIs should be calculated consistently across all reports.
The Premier Group context file contains everything Maia needs to know:
Business Overview: The scope of the dealership network.
Data Sources: Technical locations for
CAR_SALES_TRANSACTIONS,SHOWROOMS, andCAR_INVENTORY.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Detailed formulas for Revenue, Gross Profit, and Inventory Turnover.
Business Rules & Conventions: Naming standards (like
FACT_orDIM_) and data quality constraints.
Dashboard Requirements: The specific metrics required for daily and monthly reporting.
Instead of teaching Maia the same technical details every time you want to build a job, you move away from manual coordination:
|
Without Context File + Maia |
To create a Fact table, read from the tables |
|
With Context File + Maia |
Create a fact table that combines sales and inventory data. |
Why is this a Game Changer for Teams?
Because the context file holds all relevant formulas, table locations, and schema information, Maia handles the heavy lifting in the background.
This approach ensures total consistency across all your pipelines. Whether you or another developer from your team is working on the same project, Maia will always use the same naming conventions and business-approved formulas. It eliminates the risk of human drift, ensuring that Total Revenue is calculated consistently in every job, every time.
Benefits of Using Context Files and Maia Together
Situational context that is extended when necessary
For detailed standards (like complex transformation rules), you can refer to other Markdown files located elsewhere in the project and maintain the core rules in the main context files. When appropriate, Maia will dynamically refer to these while adhering to the primary context size restriction.
Project-aware and business-aware support
Instead of being generic, Maia’s responses and generated pipelines are customized to your organization’s data, terminology, and procedures by incorporating project context, glossary terms, and business rules.
More automation and less repetition
Project and business rules (such as preferred components, connection patterns, or business logic) can be “set and forgotten” with context files. You don’t have to reiterate requirements in every prompt because Maia reads all.mdfiles in.matillion/maia/rules/on each interaction.
Best Practices for Implementation
These are practical, stylistic recommendations designed to help you organize your files efficiently and maximize the accuracy of Maia’s generated workflows.
| Best Practice | Rationale & Guidance | Workflow Improvement |
|---|---|---|
|
Prioritize Focus over Length |
Keep each file short and focused. Rather than creating one massive |
Ensures clarity for the AI, making its rule interpretation faster and more accurate. Also helps manage the character limit. |
|
Maintain Agility |
Update files as your project evolves. Context Files are a living document; they should be checked into version control and updated whenever a new standard or policy is adopted. |
Prevents pipeline drift, ensuring that standards enforced by Maia always match the current business requirements. |
|
Strict Character Limit |
Maia enforces a strict 12,000-character limit across all Markdown context files within the rules directory. Maia reads these context files in alphabetical order up to the character limit. You will receive a warning error if the 12k character limit is exceeded. |
Do not try to store your entire data dictionary here. Be concise and prioritize rules over documentation. |
|
Required Storage Location |
Context Files must be stored exclusively in the following specific location within your Matillion project: |
Maia will ignore files stored anywhere else (e.g., in other project folders) and will not be applied to your prompts. |
|
Referencing External Documentation |
If you have lengthy or complex documentation (such as full business process guides, technical deep-dives, or detailed logic), it must be stored outside the rules directory. |
Use the Context File to reference a link or location to the external documentation such as |
Closing
This article explored how Matillion Context Files and Maia work together to bring consistency, governance, and speed to modern data pipelines. By converting your standards into lightweight, Markdown-based rules, Context Files provide Maia with a reliable, always-on blueprint for how jobs should be designed and named. In turn, Maia uses that context to generate and explain pipelines that follow the same business-approved logic every time, regardless of who is building them. Together, they help teams spend less time repeating instructions.
Note: Once Maia generates a pipeline, human review is still required to validate the design and confirm that all rules and standards have been correctly applied.

Looking to design or optimize Matillion DPC workflows?
If you want guidance on where Context Files and Maia fit into your broader data strategy, phData can help you assess your current environment, define scalable standards, and implement best practices tailored to your organization.
FAQs
How do Context Files interact with Git and version control in a multi-developer environment in Matillion DPC?
Context Files participate in Git operations just like the rest of your Matillion project. For example, Developer A can update a context file with a new KPI definition, build the pipeline, then commit and push their changes. Developer B pulls remote changes and uses Compare to review both pipeline and context updates together. Once merged, every developer’s Maia instance automatically applies the updated KPI definition.
Can Maia use Context Files to explain a pipeline?
Yes. Maia reads your Context Files and uses that information to explain pipelines in business and technical terms that match your documented rules.
Can Maia teach me how to be a data engineer?
Yes. In addition to Maia’s agentic capabilities of building pipelines, Maia can explain complex topics and walk you through best practices.